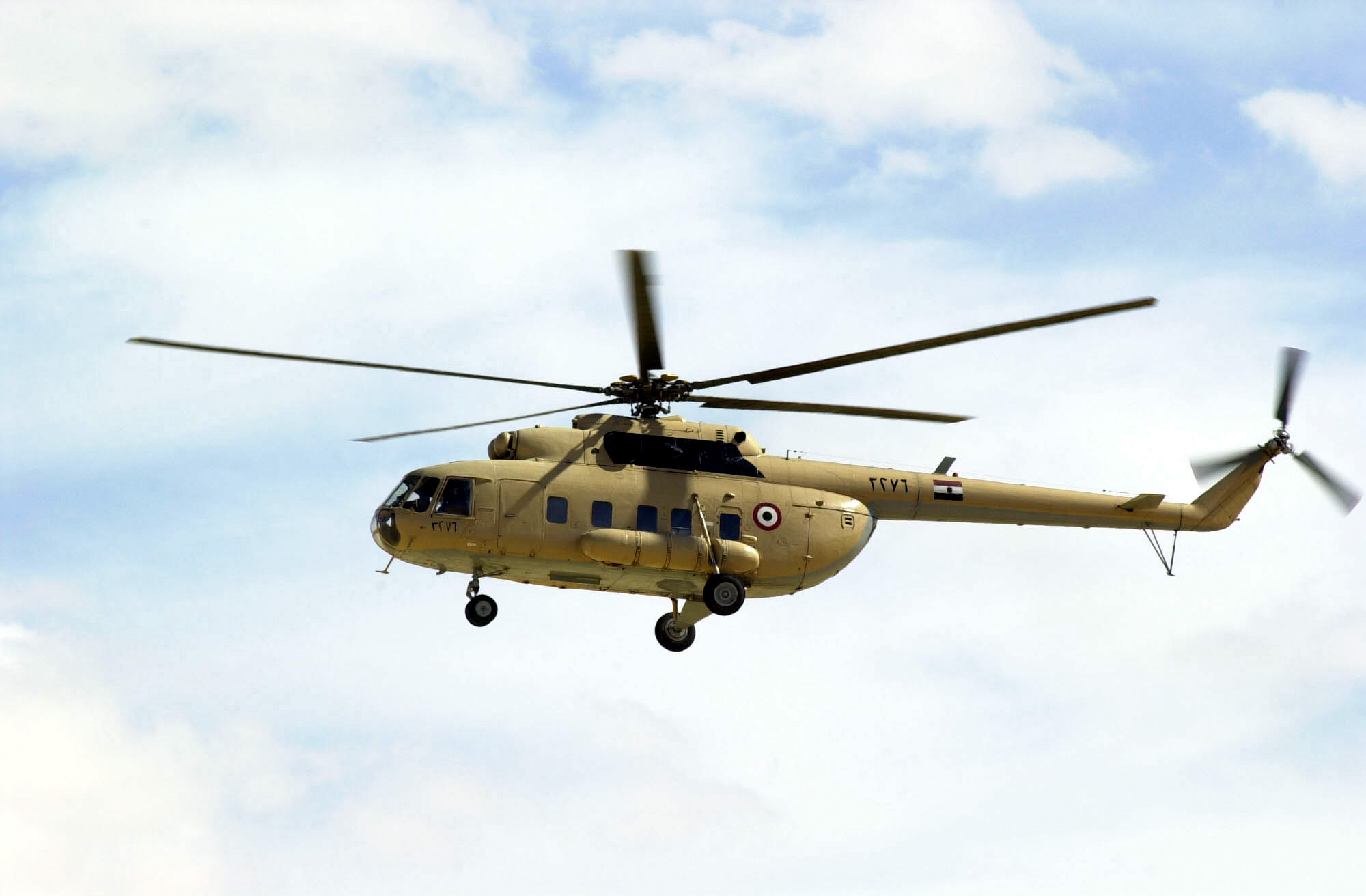
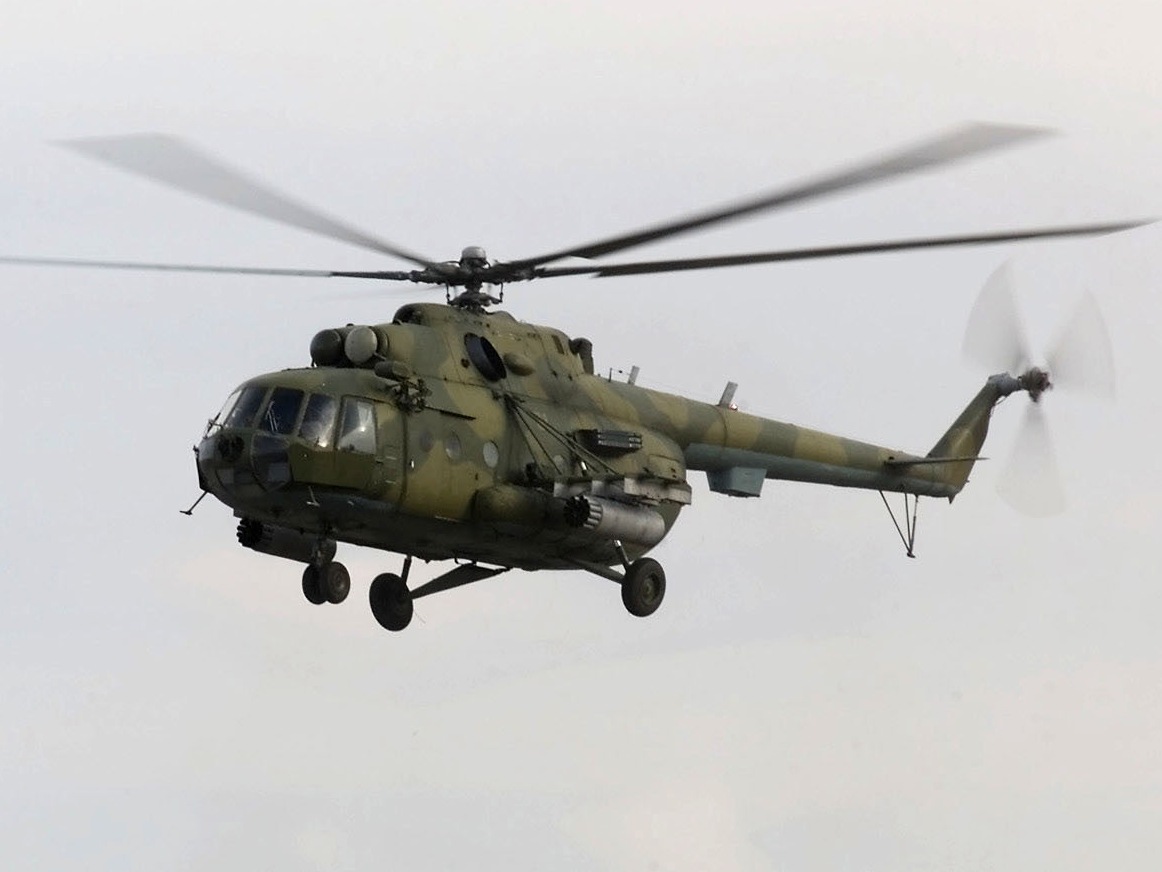
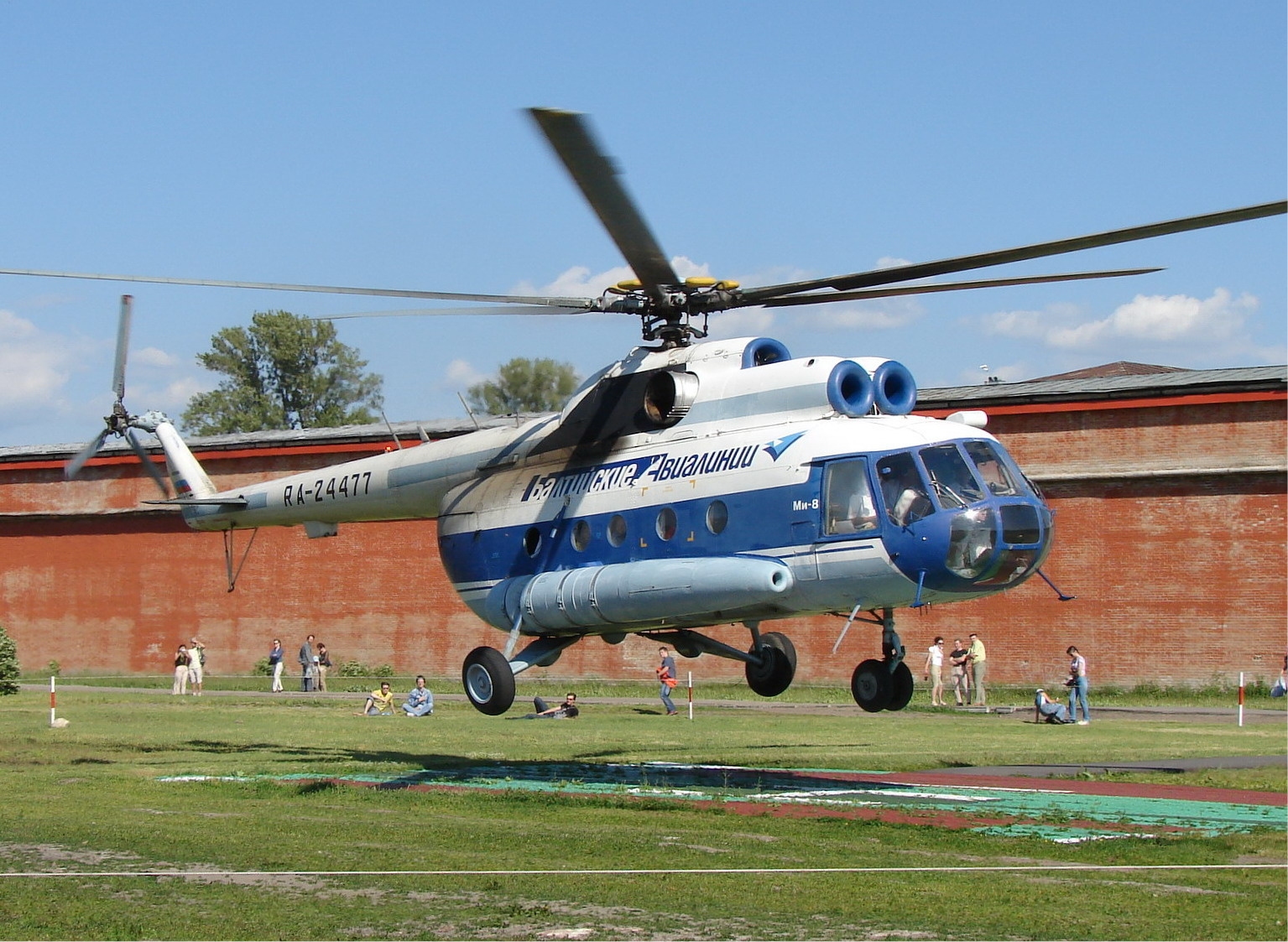
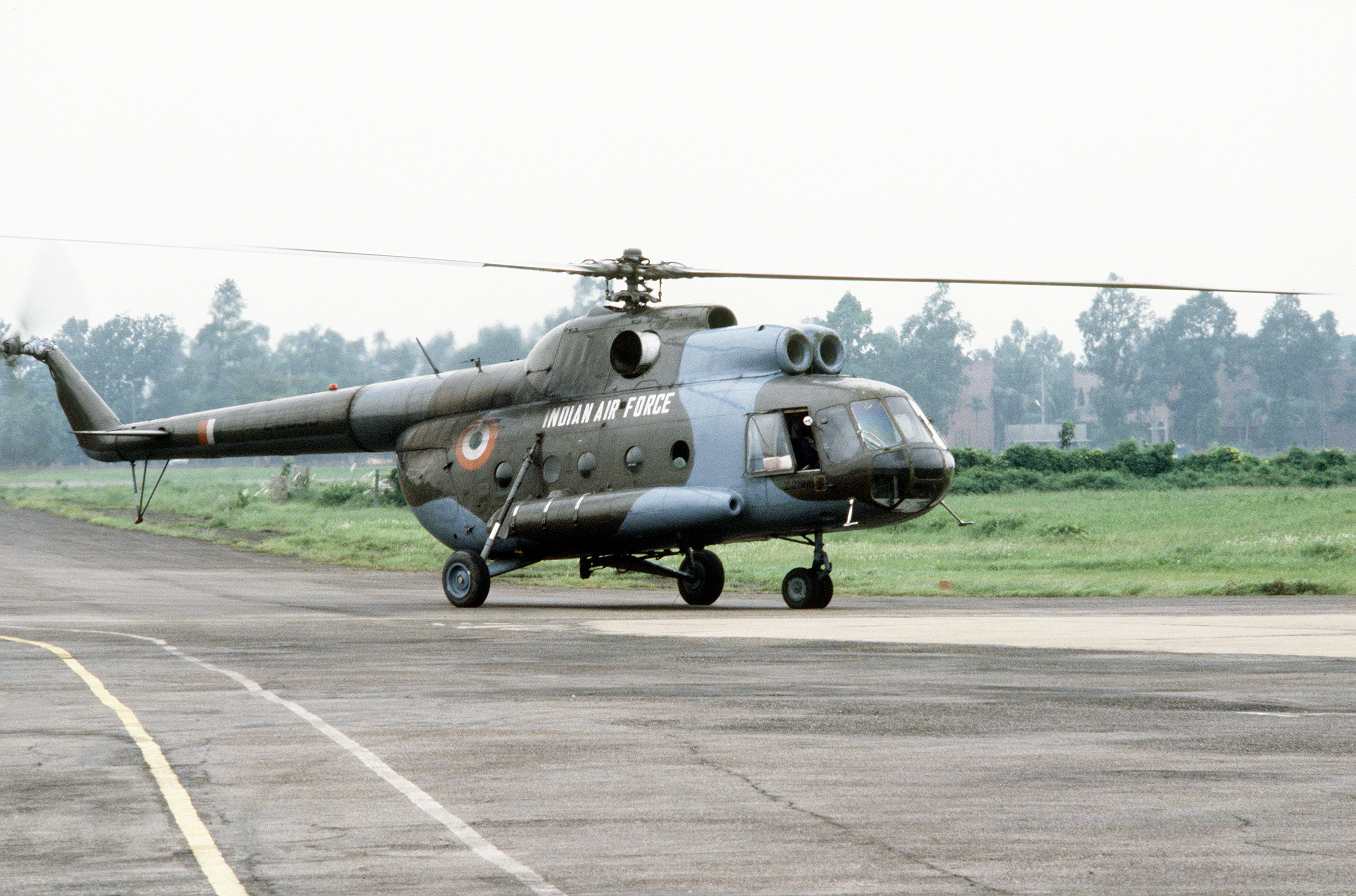
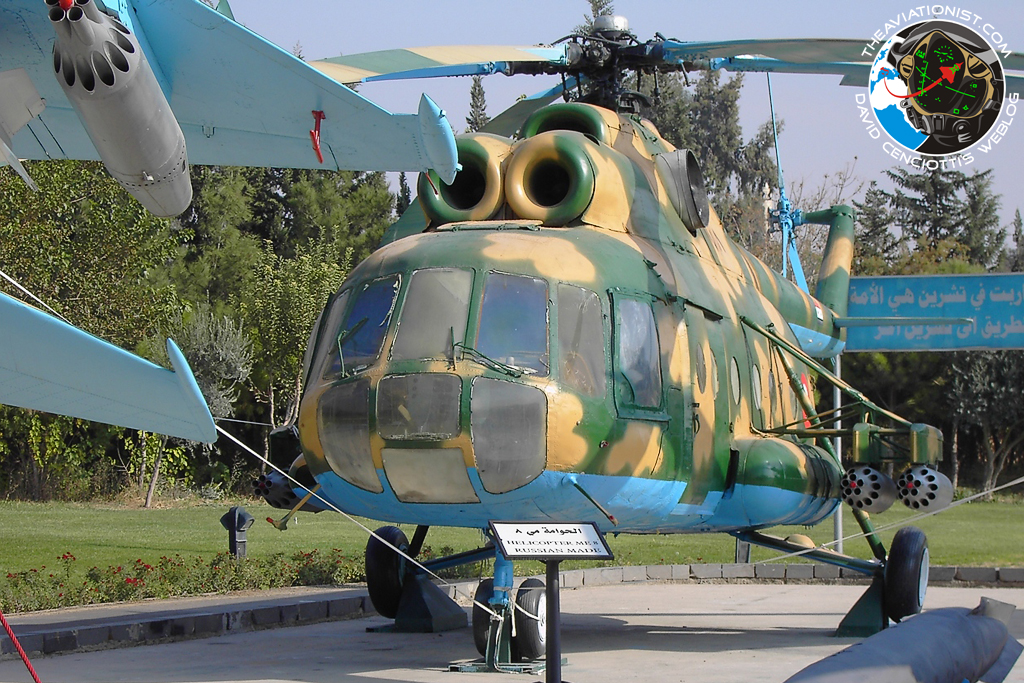
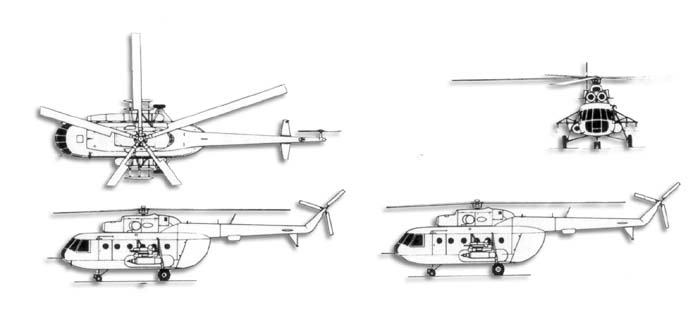
Mil Mi-8/17
- CountryRussia
- TypeMedium lift utility helicopters
- PowerplantsMi-8T - Two 1250kW (1677shp) Klimov (Isotov) TV2-117AG turboshafts driving a five blade main rotor and three blade tail rotor. Mi-17-1 - Two 1545kW (2070shp) TV3-117VM.
- PerformanceMi-8T - Max speed 250km/h (135kt), max cruising speed 225km/h (121kt). Service ceiling 14,765ft. Hovering ceiling in ground effect 5905ft, out of ground effect 2785ft. Range with standard fuel 570km (307nm), with auxiliary fuel 985km (531nm). Mi-17-1 - Max speed 250km/h (135kt), max cruising speed 230km/h (124kt). Service ceiling 18,700ft. Hovering ceiling out of ground effect 13,055ft. Range with standard fuel 570km (307nm), range with two auxiliary tanks 1065km (575nm).
- WeightsMi-8T - Empty 7149kg (15,760lb), max takeoff (for vertical takeoff) 12,000kg (26,455lb). Mi-17-1 - Empty equipped 7055kg (15,555lb), max takeoff 13,000kg (28,660lb).
- DimentionsMi-8T - Main rotor diameter 21.29m (69ft 10in), length overall 25.24m (82ft 10in), fuselage length 18.17m (59ft 8in), height 5.54m (18ft 2in). Main rotor disc area 356.0m2 (3932sq ft). Mi-17-1 - Same except for length overall 25.35m (83ft 2in), fuselage length 18.42m (60ft 6in).
- CapacityFlightcrew of two, with provision for flight engineer. Primarily used for freight transport, internal and/or with external sling loads. Can carry up to 32 passengers in Mi-8, or 24 in Mi-8T. Mi-8 Salon executive version seats 11 passengers. As air ambulance can accommodate 12 stretchers.
- ProductionOver 12,000 Mi-8s and Mi-17s built, but majority for military service.
Implicit more prominent numbers than another Russian helicopter, the Mi-8/Mi-17 arrangement (NATO codename "Hip") was outlined essentially as a military transport, yet is likewise in far reaching common utilization.
The Mi-8 was planned as a trade for the cylinder engined Mi-4, with outline work starting in May 1960. To start with flight of the model (controlled by a solitary Soloviev turboshaft driving a four cutting edge fundamental rotor) happened in June 1961, while a creation standard Mi-8 flew in August 1962 and generation started without further ado subsequently. Adaptations of the Mi-8 constructed for common utilization have square windows and incorporate the Mi-8p traveler variant, Mi-8t utility transport, Mi-8tm overhauled traveler transport with climate radar and Mi-8s Salon official transport.
Creation of the Mi-8 stopped for the re-engined Mi-17, which was first freely uncovered to the west at the 1981 Paris Airshow. The Mi-17 presented Tv3 turboshafts and the tail rotor was moved to the port side of the tailboom. Common adaptations incorporate the base Mi-17, and the basically comparable Mi-17-1 and Mi-17m, which both peculiarity all the more compelling Tv3-117vm turboshafts, and are assembled by Ulan Ude Aviation and Kazan Helicopters individually. Both have been heartily showcased in the west.
The Kazan/Mil created Mi-17kf Kittiwake is intended to meet western certificate gauges and peculiarities an EFIS instrument board with shade shows, outlined and incorporated by Kelowna Flightcraft in Canada, adjusted "dolphin" nose with space for radar, and a back stacking incline set up of the clamshell entryways. The recent two peculiarities are likewise consolidated on the Kazan/Mil Mi-17md and Mi-17n.